1. Why blockchain is trustworthy?
Blockchain is a peer-to-peer network that has its consensus algorithm. The main reason behind its trustworthiness is how it stores and deal with data. It uses cryptographic algorithms to ensure that the data is protected against any third party malicious actor. This means only the entity that owns the data will be able to access it. Also, the data stores in the blockchain can be traced anytime which brings in transparency. One more thing that makes blockchain trustworthy is the data integrity feature. With this feature, data cannot be changed after it is written.
Note: This is one of the most common questions about blockchain.
2. What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a decentralized system just like bitcoin. It is completely decentralized which means that there is no centralized authority controlling it. It is developed by Vitalik Buterin and uses a different approach when compared to bitcoin. Just like bitcoin, digital payments can be done on the platform. It uses smart contracts to automate legal contracts within two peers. dApps(decentralized apps) is an app that runs on Ethereum and use smart contracts to manage an organization or a specific part of the project.
3. Why is Blockchain a trusted approach?
• Blockchain can be trusted due to so many reasons.
• Its compatibility with other business applications due to its open-source nature.
• Its security. As it was meant for online transactions, the developers have paid special attention to keeping up the pace when it comes to its security.
• It really doesn’t matter what type of business one owns, Blockchain can easily be considered.
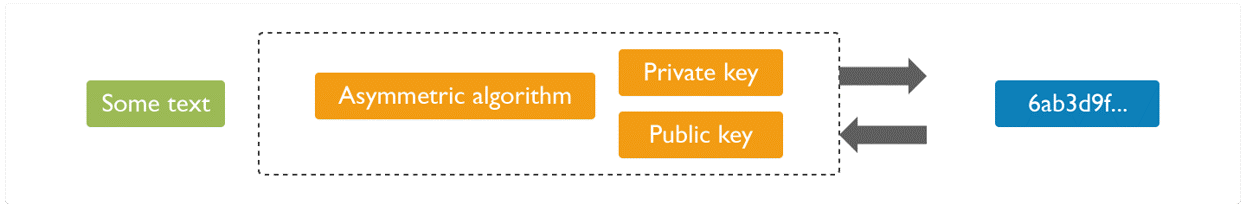
4. What is encryption? What is its role in Blockchain?
Data security always matters. Encryption is basically an approach that helps organizations to keep their data secure. The encrypted data is encoded or changed up to some extent before it is sent out of a network by the sender and only authorized parties can access that information.In Blockchain, this approach is useful because it simply adds more to the overall security and authenticity of blocks and helps to keep them secure.
5. What do you mean by blocks in the blockchain technology?
Blockchain consists of a list of records. Such records are stored in blocks. These blocks are in turn linked with other blocks and hence constitute a chain called Blockchain.
BLOCK CHAIN TRAINING
Weekend / Weekday Batch
6. How does a block is recognized in the Blockchain approach?
Every block in this online ledger basically consists of a hash pointer which acts as a link to the block which is prior to it, transaction data and in fact a stamp of time.
7. Is it possible in Blockchain to remove one or more block from the networks?
Yes, it can be done. There are times when only a specific portion of this online ledger is to be considered. With the help of default options and filters, this can easily be done without making a lot of efforts.
8. What is public blockchain? Give examples.
A public blockchain is public in nature. They are entirely decentralized where anyone can read, write and join. No central authority controls the blockchain. Also, all the data can be validated as data once are written cannot be altered. Key examples of public blockchains include bitcoin and ethereum.
9. What is private blockchain? Give examples.
A private blockchain is private in nature. They operate with a central authority in control. This way they allow access to the blockchain only to selected users. It is not accessible to everyone which makes it ideal for banks and other centralized organizations. Example, Hyperledger.
10. What is federated blockchain? Give examples
Federated blockchain is a blockchain that is run by a group. This makes them faster and scalable as the group dedicates the validation of the transactions. To get started, pre-selected nodes are made leaders. These nodes that dictate both the transactions and also the persons that can participate in the blockchain. Example include EWF, R3, etc.
Federated Blockchain Simply Explained